Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it? This respiratory virus, Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), is causing increasing concern among health officials and parents alike. Understanding its transmission, symptoms, and potential long-term effects is crucial for effective prevention and management. This surge in cases highlights the need for increased public awareness and improved healthcare strategies to combat this growing threat to children’s health in China.
HMPV, a member of the paramyxoviridae family, primarily affects the lower respiratory tract. Infection typically presents with cold-like symptoms, but can progress to more severe conditions, especially in young children and those with pre-existing respiratory issues. The recent increase in cases in China warrants a closer examination of the contributing factors, including potential changes in viral strains, environmental conditions, and healthcare access.
Worried about the HMPV surge in China? It’s a nasty virus hitting kids hard. Need to explain this clearly in your next podcast? Check out this guide on finding the right AI voice generator for podcasting to make your content engaging and accessible. Understanding and explaining HMPV effectively is crucial, so use the right tools to get your message across.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) in China: A Rising Concern: Viral Disease HMPV Is On The Rise Among Kids In China — What Is It?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus causing increasing concern, particularly among children in China. Understanding its characteristics, transmission, impact, and management is crucial for effective public health strategies.
Understanding Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
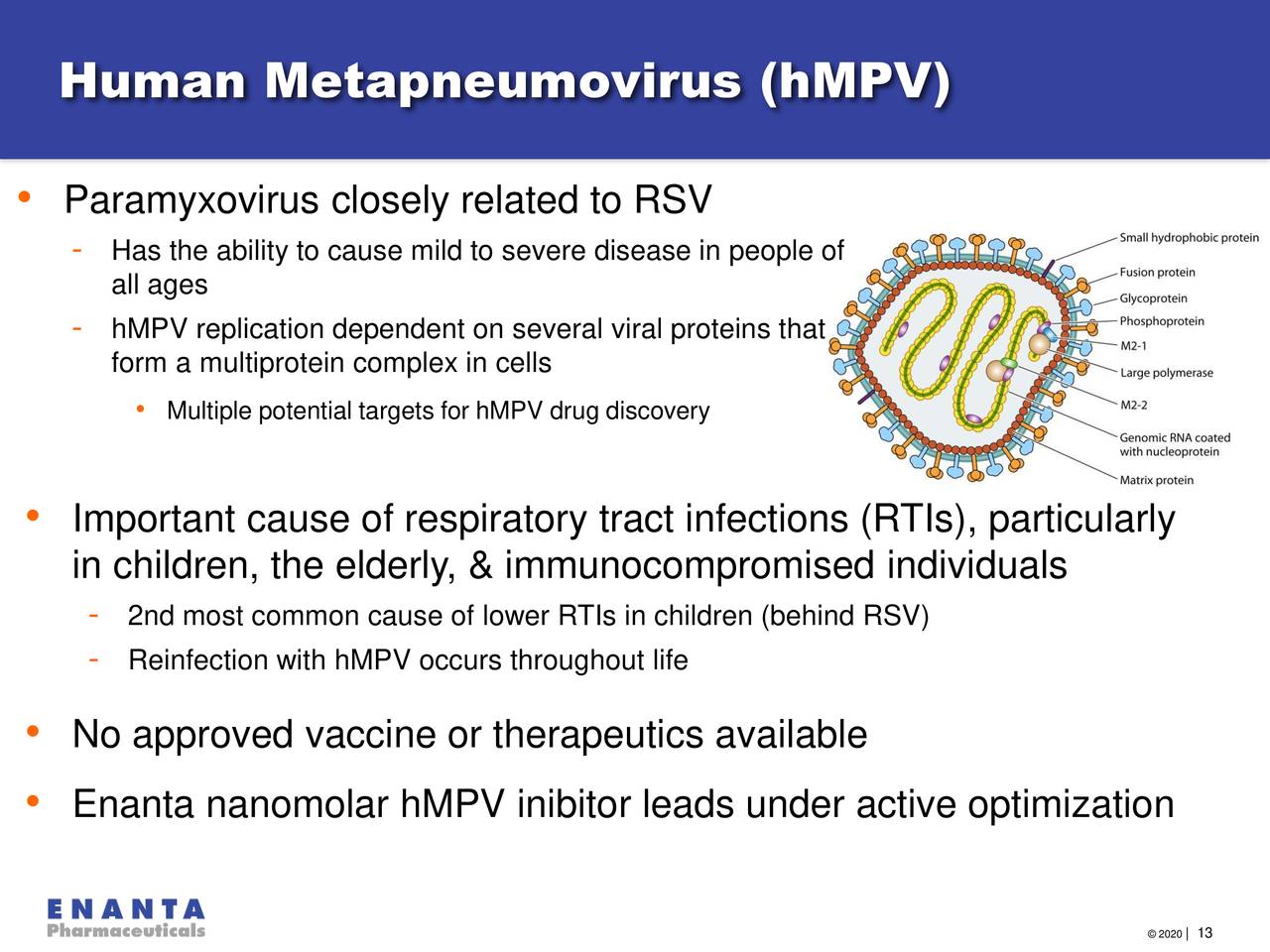
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family, subfamily Pneumovirinae. It shares structural similarities with other pneumoviruses like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). HMPV’s genome encodes several proteins responsible for viral replication, attachment to host cells, and evasion of the immune system. Infection occurs when the virus binds to receptors on respiratory epithelial cells, initiating replication and leading to the release of new viral particles that infect other cells.
This process causes inflammation and damage to the respiratory tract, resulting in various symptoms.
HMPV Symptoms in Children
HMPV infection in children presents with a range of symptoms, varying in severity depending on the child’s age and overall health. The following table summarizes common symptoms and treatment considerations.
So, HMPV is hitting kids hard in China right now – it’s a respiratory virus causing a lot of concern. Completely unrelated, but while we’re on the news, check out this story: Republican Mike Johnson reelected House speaker after dramatic political maneuvering. Anyway, back to HMPV – parents should be aware of the symptoms and seek medical advice if needed.
| Age Group | Common Symptoms | Severity | Treatment Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infants (0-6 months) | Cough, fever, difficulty breathing, wheezing, apnea | Can range from mild to severe, potentially requiring hospitalization | Supportive care, including oxygen therapy and respiratory support if needed |
| Young Children (6 months – 5 years) | Runny nose, cough, fever, sore throat, headache, muscle aches | Generally mild, but can progress to bronchiolitis or pneumonia in some cases | Supportive care, including rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers |
| Older Children (5-12 years) | Mild cold-like symptoms, similar to a common cold | Usually mild and self-limiting | Supportive care, focusing on symptom relief |
Transmission and Spread of HMPV
HMPV primarily spreads through close contact with respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces. Factors like overcrowding, poor hygiene, and weakened immune systems contribute to its spread, particularly in childcare settings. While similar to RSV and influenza in its transmission mode, HMPV’s peak season may differ slightly.
Effective prevention relies on reducing exposure to infected individuals and maintaining good hygiene practices.
- Frequent handwashing
- Avoiding close contact with sick individuals
- Disinfecting frequently touched surfaces
- Promoting good respiratory hygiene (covering coughs and sneezes)
- Staying home when sick
HMPV’s Impact on Children’s Health in China
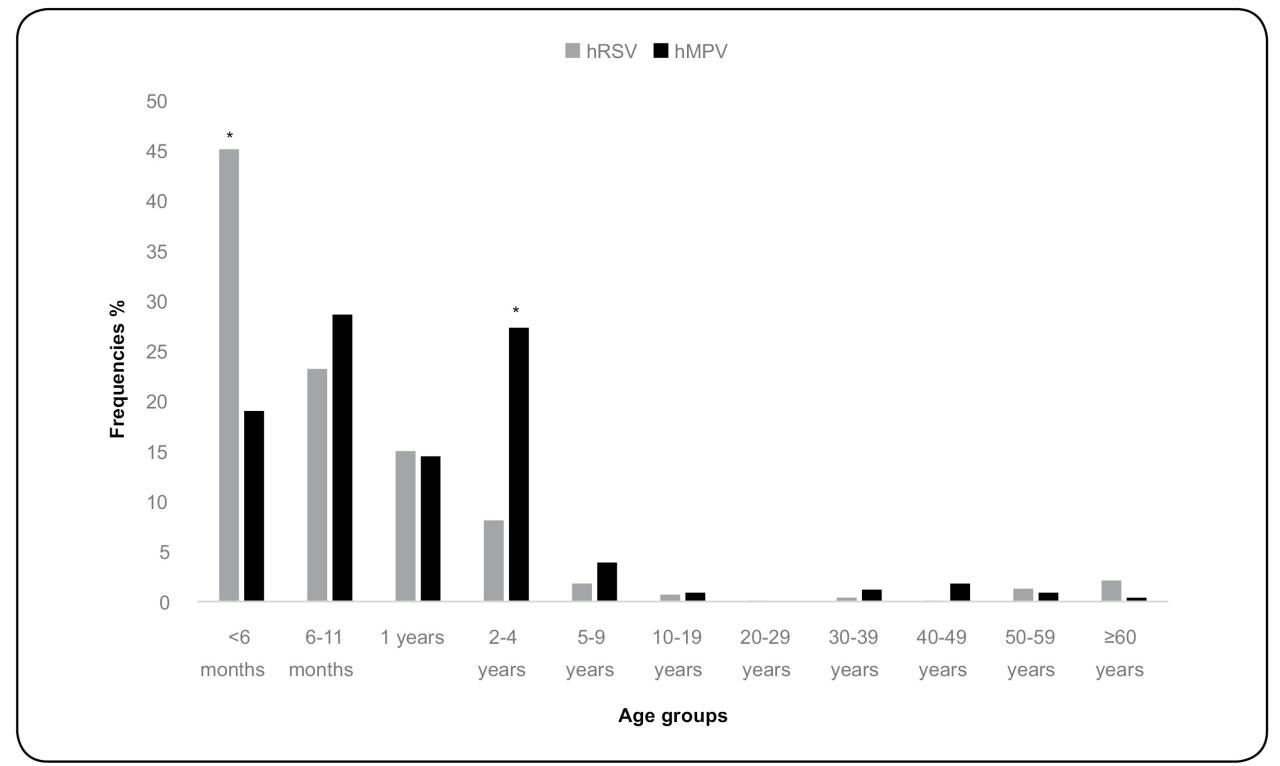
Data on the precise prevalence and severity of HMPV infections in China are still emerging, and vary regionally. However, there are indications of a recent surge in cases, potentially linked to factors such as increased population density in urban areas, changing climate patterns, and reduced immunity following the COVID-19 pandemic. This increase puts a strain on healthcare resources, increasing hospitalization rates and treatment costs.
Effective public health communication is vital to mitigate the impact.
| Region | Age Group | Hospitalization Rates (Illustrative Example) | Mortality Rates (Illustrative Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Under 5 years | 2% | <0.1% |
| Shanghai | Under 5 years | 1.5% | <0.1% |
| Guangzhou | Under 5 years | 2.5% | <0.1% |
A public health communication strategy should focus on simple, clear messages disseminated through various channels (e.g., social media, community health centers, schools) emphasizing hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and seeking medical attention for severe symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment of HMPV
HMPV infection is typically diagnosed using molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or rapid antigen detection tests. Currently, there’s no specific antiviral treatment for HMPV; management focuses on supportive care to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Research into antiviral therapies and vaccines is ongoing.
- Rest
- Hydration (fluids)
- Over-the-counter pain and fever reducers (as appropriate)
- Oxygen therapy (if needed)
- Nebulized treatments (if needed)
Long-Term Effects and Complications of HMPV
While most HMPV infections resolve without long-term consequences, some children may experience ongoing respiratory issues. The table below compares short-term and long-term effects.
| Short-Term Effects | Long-Term Effects |
|---|---|
| Cough, fever, runny nose, wheezing, difficulty breathing | Wheezing, recurrent respiratory infections, increased risk of asthma or other respiratory conditions |
Premature infants, children with underlying respiratory conditions, and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of severe HMPV infection.
Illustrative Examples of HMPV Infection, Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it?
A hypothetical case: A 6-month-old infant presents with fever, persistent cough, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis via PCR confirms HMPV infection. The infant requires hospitalization for supportive care, including oxygen therapy. After a week, the infant’s condition improves, and he is discharged.
Hey, so you’re wondering about this HMPV virus surge in China, right? It’s causing a lot of concern, especially with kids. To understand it better, check out this article explaining the recent “Covid-like” outbreak: What is HMVP virus, Chinas recent ‘Covid-like outbreak’, should. Knowing more about the broader context of viral outbreaks in China will definitely help you grasp the HMPV situation better.
Basically, it’s a good idea to stay informed about these things!
Microscopic appearance: HMPV is pleomorphic, ranging from spherical to filamentous. It has a lipid envelope studded with glycoproteins, including the fusion (F) and attachment (G) proteins, which are crucial for viral entry into host cells. The nucleocapsid, containing the viral RNA genome, is located within the envelope.
Visual representation: Imagine a small, irregularly shaped virus particle approaching a respiratory cell. The viral glycoproteins on its surface interact with receptors on the cell membrane. The virus then fuses with the cell membrane, releasing its genetic material into the cytoplasm of the respiratory cell, where it hijacks the cell’s machinery to produce more viruses.
Conclusive Thoughts
The rise of HMPV infections in Chinese children underscores the importance of proactive measures to protect vulnerable populations. While supportive care remains the cornerstone of treatment, increased research into antiviral therapies and vaccines is vital. Educating parents and healthcare providers about prevention strategies, early diagnosis, and appropriate management is key to mitigating the impact of this growing public health challenge.
By understanding HMPV’s transmission dynamics and potential long-term consequences, we can work towards a future where children in China are better protected from this respiratory threat.
Question Bank
What is the incubation period for HMPV?
The incubation period for HMPV is typically 2-6 days.
Is HMPV contagious?
Yes, HMPV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets.
Are there any long-term effects of HMPV infection?
While most children recover fully, some may experience wheezing or other respiratory issues in the long term. A link to asthma development has also been investigated.
How is HMPV diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves PCR testing of respiratory samples.