How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to advanced technological applications. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and safely.
We’ll explore the fundamental controls, delve into different flight modes, and offer practical advice on navigating various challenges, including wind compensation and troubleshooting common issues. Furthermore, we’ll examine the legal framework surrounding drone operation and discuss the ethical responsibilities involved. By the end of this guide, you’ll possess a comprehensive understanding of how to operate a drone effectively and responsibly.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and a thorough understanding of its controls, and you can find a comprehensive guide on this very topic at how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and adherence to safety guidelines.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and potential legal issues. This section details a comprehensive checklist and emphasizes the importance of each step.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should be followed diligently before each flight. This ensures the drone is in optimal condition and reduces the risk of malfunctions.
- Battery Check: Verify the battery is fully charged and properly connected. Check for any signs of damage, swelling, or leakage.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, bends, or other damage. Replace any damaged propellers.
- GPS Signal Verification: Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. The number of satellites acquired should be sufficient for stable flight.
- Gimbal Calibration (if applicable): If your drone has a gimbal, calibrate it to ensure smooth camera movement.
- Radio Controller Check: Verify the controller’s batteries are charged and the connection to the drone is stable.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts or damage.
- Software Updates: Ensure the drone’s firmware is up-to-date to benefit from the latest features and bug fixes.
- Flight Environment Assessment: Check weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and potential obstacles in the flight area.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure aids in remembering each critical step. The following flowchart Artikels the process:
(Illustrative description of a flowchart: The flowchart would start with “Begin,” then branch to “Battery Check,” “Propeller Inspection,” “GPS Signal Check,” and “Visual Inspection.” Each check would have a “Pass” or “Fail” outcome. “Fail” would lead to troubleshooting and repair, while “Pass” would lead to the next check. The final step would be “Ready for Takeoff.”)
Drone Battery Comparison
Different drone batteries offer varying flight times and safety considerations. Understanding these differences is vital for choosing the right battery and ensuring safe operation.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone effectively and responsibly. Mastering these skills ensures safe and successful flights, maximizing the potential of your drone.
| Battery Type | Voltage | Flight Time (Approximate) | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | 7.4V – 22.2V (varies widely) | 15-30 minutes (depending on drone and usage) | Avoid overcharging, overheating, and short circuits. Store in a fire-safe container. |
| LiFe (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 7.4V – 22.2V (varies widely) | Similar to LiPo, but potentially slightly less | Less prone to thermal runaway than LiPo, but still require careful handling. |
| LiHV (High Voltage LiPo) | 8.4V – 25.2V (varies widely) | Slightly longer flight times than standard LiPo | Similar safety precautions as LiPo batteries. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding the basic controls and navigation of your drone is paramount for safe and efficient operation. This section explains the fundamental controls and different flight modes.
Drone Controls, How to operate a drone
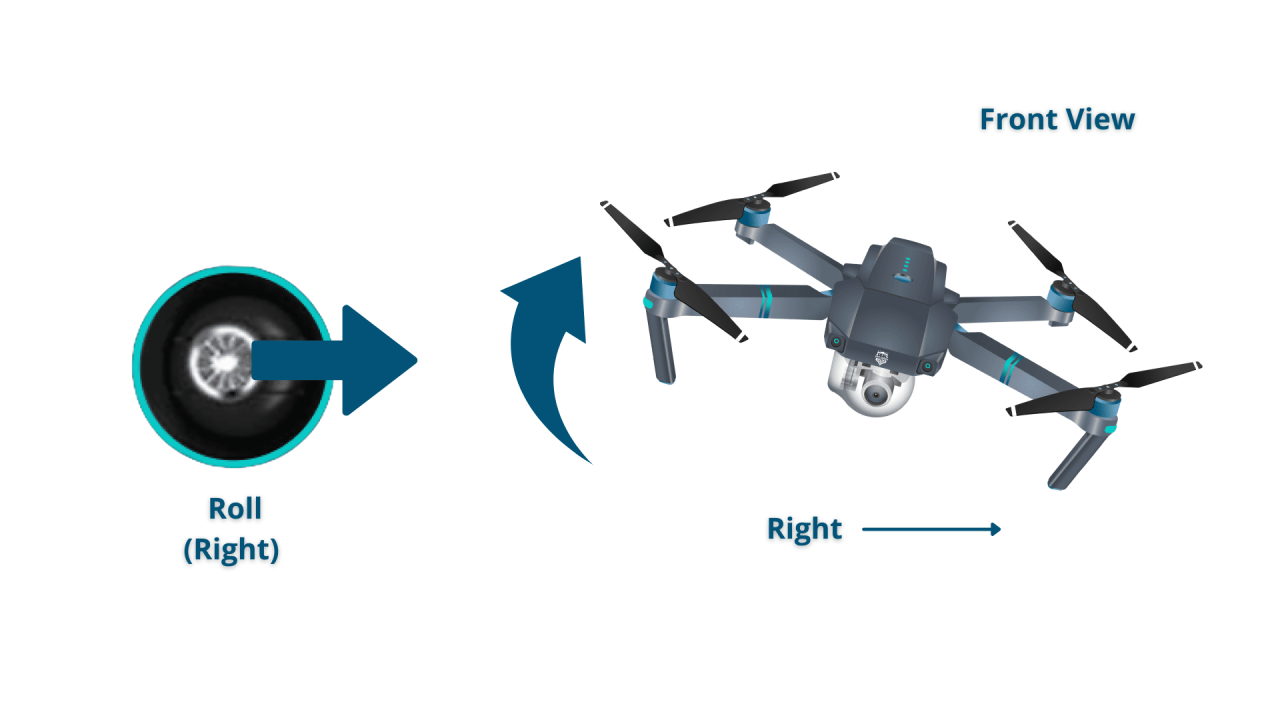
Most drones use a four-channel control system. These channels control the drone’s movement in four dimensions: Throttle, Yaw, Pitch, and Roll.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s sideways movement (left and right).
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents. These steps should be followed meticulously.
- Pre-flight checks completed: Ensure all pre-flight checks have been successfully completed.
- Choose a safe location: Select a clear, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Level the drone: Ensure the drone is level before takeoff.
- Initiate takeoff: Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Hover: Practice hovering the drone steadily before moving it.
- Landing: Gently lower the throttle to bring the drone down slowly and smoothly.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding these modes is important for adapting to different flying conditions.
- GPS Mode: Provides stable flight using GPS data. Ideal for beginners and calm conditions.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to its initial position, regardless of GPS signal. Useful for indoor flight or when GPS is weak.
- Sport Mode (if available): Offers increased responsiveness and speed, suitable for experienced pilots.
Drone Control Interface Comparison
Different drone models may have slightly different control interfaces, but the fundamental principles remain consistent. However, features like customizable control mappings and different screen layouts can impact the user experience.
(Illustrative comparison: A comparison would highlight differences in the physical layout of controllers (e.g., joystick placement, button arrangement), the software interface (e.g., screen size, information displayed), and the availability of features like flight simulation or assisted flight modes.)
Mastering Drone Flight Techniques
Developing smooth and controlled drone movements requires practice and understanding of fundamental techniques. This section offers tips for achieving precise maneuvers and handling challenging conditions.
Smooth and Controlled Movements
Achieving smooth and controlled movements involves gentle and precise control inputs. Avoid abrupt movements, especially when close to obstacles.
- Use small, incremental adjustments: Make small adjustments to the controls rather than large, sudden movements.
- Anticipate wind conditions: Account for wind effects on the drone’s movement.
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice is key to developing smooth and controlled flight.
Basic Maneuvers

Mastering basic maneuvers is essential for safe and effective drone operation. These maneuvers form the foundation of more complex flight techniques.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing the drone’s altitude smoothly.
- Descending: Decreasing the drone’s altitude smoothly.
- Turning: Rotating the drone smoothly and precisely.
Wind Compensation
Wind significantly impacts drone flight. Effective wind compensation involves adjusting the controls to counteract wind effects and maintain stability.
(Illustrative explanation: Pilots need to anticipate wind direction and strength. They must compensate by adjusting the controls to maintain position or trajectory. For example, a headwind requires more throttle to maintain altitude, while a crosswind requires adjustments to yaw and roll to stay on course.)
Common Piloting Mistakes
Understanding common piloting mistakes helps avoid potential accidents and damage. This list highlights frequent errors and provides solutions.
- Abrupt control inputs: Avoid jerky movements, use smooth and gradual inputs.
- Ignoring wind conditions: Always account for wind when planning and executing a flight.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles.
- Losing visual contact with the drone: Maintain visual contact at all times.
- Disregarding battery levels: Monitor battery levels closely and land before the battery is critically low.
Aerial Photography and Videography

Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. This section details settings adjustments, composition techniques, and cinematic shot creation.
Optimal Image and Video Capture Settings
Adjusting camera settings is crucial for obtaining high-quality images and videos. These settings depend on the lighting conditions and desired aesthetic.
- ISO: Adjust ISO based on lighting conditions; lower ISO in bright light, higher ISO in low light.
- Shutter Speed: Maintain a proper shutter speed to avoid motion blur; generally, use a shutter speed that is twice the frame rate.
- Aperture: Adjust aperture for depth of field; wider aperture for shallow depth of field, narrower aperture for greater depth of field.
- White Balance: Set white balance to match the lighting conditions for accurate color reproduction.
Effective Shot Composition
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of aerial shots. Using the rule of thirds and leading lines improves the overall impact.
(Illustrative description: The rule of thirds involves placing key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds, both horizontally and vertically. Leading lines use natural elements like roads or rivers to draw the viewer’s eye into the scene.)
Creating Cinematic Shots
Using various flight techniques creates dynamic and visually engaging cinematic shots. Smooth movements and creative camera angles enhance the overall aesthetic.
(Illustrative description: Techniques include smooth, slow pans and tilts, tracking shots following a subject, and creative use of altitude and perspective. The use of cinematic flight modes, if available on the drone, is also beneficial.)
Creating Time-Lapse Videos
Time-lapse videos capture the passage of time in a condensed format, creating stunning visual effects. A methodical approach is crucial for creating a smooth and engaging time-lapse.
- Plan your shots: Choose a location and composition that will change significantly over time.
- Set up your drone: Ensure the drone is stable and securely positioned.
- Configure the interval: Set the interval between shots based on the desired speed of the time-lapse.
- Start recording: Initiate the time-lapse recording and let it run for the desired duration.
- Post-processing: Use video editing software to assemble the individual shots into a cohesive time-lapse video.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its reliable operation. This section provides a maintenance schedule and troubleshooting guidance.
Regular Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent potential problems and extends the drone’s operational life. This schedule Artikels key maintenance tasks.
- Weekly: Inspect propellers, check for loose parts, clean the drone body.
- Monthly: Check battery health, inspect motor mounts and gimbal (if applicable).
- Quarterly: Perform a thorough inspection of all components, calibrate sensors and GPS.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing common drone issues promptly prevents further damage and ensures continued safe operation. This section details troubleshooting steps for common problems.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with a stronger GPS signal; check for obstructions.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage; replace any faulty motors.
- Gimbal Issues (if applicable): Calibrate the gimbal; check for any physical obstructions.
Causes and Solutions for Drone Malfunctions
Understanding the potential causes of drone malfunctions helps in effective troubleshooting. This section identifies common causes and their corresponding solutions.
(Illustrative examples: A drone might malfunction due to low battery voltage, GPS signal interference, motor failure, or software glitches. Troubleshooting would involve checking battery levels, relocating to an area with better GPS reception, inspecting motors for damage, and checking for software updates.)
Proper Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect the drone from damage and extend its lifespan. These practices ensure the drone remains in optimal condition.
- Storage: Store the drone in a dry, cool, and dust-free environment.
- Transportation: Use a protective case to prevent damage during transportation.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires adherence to local laws and regulations. This section highlights key legal considerations and airspace restrictions.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and are subject to change. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws in your area before operating a drone.
(Illustrative example: Regulations might include registration requirements, restrictions on flight altitude and distance, limitations on flying near airports or sensitive areas, and requirements for obtaining permits for certain operations.)
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones are areas where drone operation is prohibited or restricted. It’s crucial to check for these zones before flying.
(Illustrative description: These zones are often established near airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Online tools and apps are available to help identify these restricted areas.)
Drone Registration and Permits
Many jurisdictions require drone registration and may require permits for certain operations. It’s essential to understand and comply with these requirements.
(Illustrative example: Registration often involves providing identifying information about the drone and its owner. Permits might be required for commercial operations or flights in specific locations.)
Restricted or Prohibited Scenarios
Several scenarios may restrict or prohibit drone operation. These scenarios need to be considered before flight.
- Flying near airports or airfields: Strict regulations often apply to flying near airports.
- Flying over crowds or populated areas: This poses safety risks and is often prohibited.
- Flying at night without proper lighting: Night flights require additional safety measures and may be restricted.
- Flying in adverse weather conditions: Flying in strong winds, rain, or fog is dangerous and should be avoided.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible decision-making. From the meticulous pre-flight checks to the creative possibilities of aerial photography, each step contributes to a safe and enjoyable experience. Remember, consistent practice, adherence to safety guidelines, and a thorough understanding of the legal framework are crucial for responsible drone piloting. Embrace the learning process, and soon you’ll be soaring through the skies, capturing stunning visuals, and exploring the endless applications of this exciting technology.
Common Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and comprehensive tutorials.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if operating near magnetic interference sources. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
If GPS signal is lost, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, carefully land the drone in a safe, open area.
How do I handle strong winds during drone operation?
Avoid flying in high winds. If unavoidable, fly into the wind for stability and use lower speeds and gentler maneuvers.
